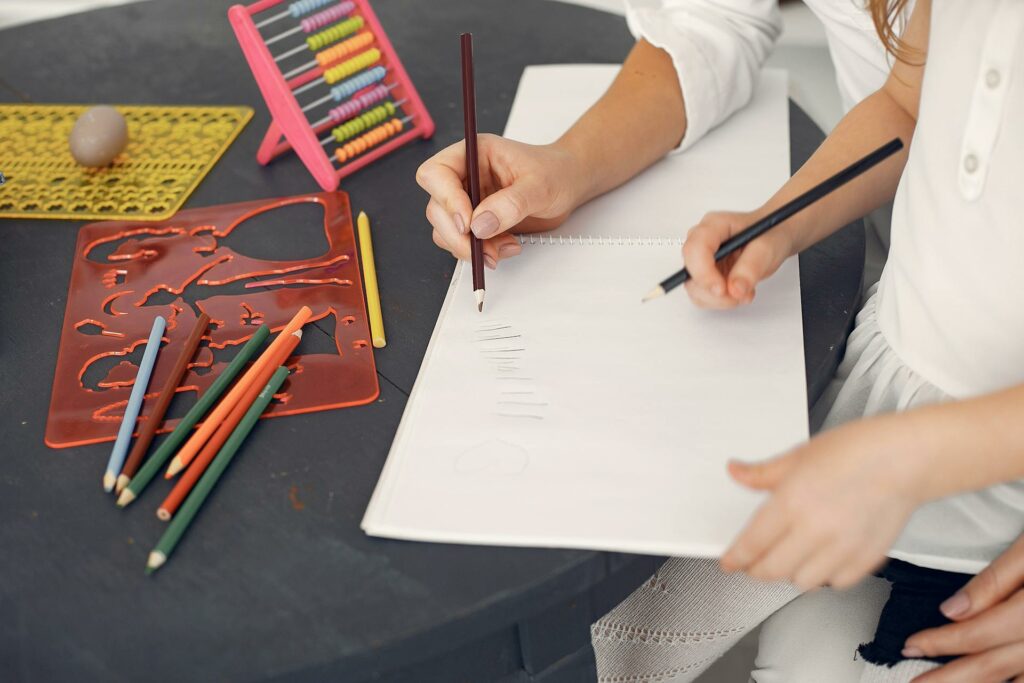
Arithmetic forms the cornerstone of mathematics, providing essential skills for everyday life and building a strong foundation for advanced mathematical concepts. Teaching basic arithmetic isn’t just about learning numbers; it’s about developing problem-solving abilities, logical thinking, and numeracy skills that are crucial in our modern world. In this blog post, we’ll explore the importance of teaching basic arithmetic and effective strategies to make learning engaging and meaningful.
Why Teach Basic Arithmetic?
Basic arithmetic encompasses fundamental operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These skills are essential for various practical applications:
- Everyday Mathematics: From managing finances to measuring ingredients for recipes, arithmetic is part of our daily routines.
- Problem Solving: From managing finances to measuring ingredients for recipes, arithmetic is part of our daily routines.
- Critical Thinking: Understanding arithmetic concepts fosters logical thinking and analytical skills.
- Career Readiness: Many professions require a strong grasp of arithmetic, such as engineering, finance, and computer science.
Importance of Basic Arithmetic Mastery
Mastering basic arithmetic is crucial for several reasons beyond its practical applications:
Academic Success: Proficiency in arithmetic sets the stage for success in more complex mathematical concepts taught in later grades.
Confidence Building: Proficiency in arithmetic sets the stage for success in more complex mathematical concepts taught in later grades.
Critical Thinking Development: Arithmetic requires logical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are transferable to various academic and real-life scenarios.
Numeracy Skills: A solid arithmetic foundation enhances numeracy skills, enabling individuals to interpret data, make informed decisions, and navigate everyday challenges.
Strategies for Teaching Basic Arithmetic
- Hands-On Activities:
-Use manipulatives like counters, blocks, or coins to illustrate concepts like addition and subtraction.
-Encourage students to solve real-life problems using these tools to make learning tangible and interactive. - Visual Representations:
-Employ visual aids such as number lines, arrays, or bar models to demonstrate multiplication and division.
-Visualizing problems helps students grasp abstract concepts and enhances comprehension. - Real-World Applications:
-Visualizing problems helps students grasp abstract concepts and enhances comprehension.
-Show how arithmetic is used in various professions to highlight its relevance and utility. - Games and Puzzles:
-Incorporate games like bingo, card games, or digital math puzzles to make learning enjoyable.
-Gamified activities enhance engagement and motivate students to practice arithmetic skills. - Peer Collaboration:
-Encourage peer-to-peer learning through group activities and discussions.
-Collaborative learning fosters communication skills and allows students to learn from each other. - Progressive Learning:
-Collaborative learning fosters communication skills and allows students to learn from each other.
-Collaborative learning fosters communication skills and allows students to learn from each other. - Differentiated Instruction:
-Tailor instruction to accommodate diverse learning styles and abilities.
-Offer varied approaches, such as visual, auditory, and kinaesthetic methods, to cater to individual needs. - Reinforcement and Practice:
-Provide ample opportunities for practice through worksheets, online exercises, and hands-on activities.
-Regular reinforcement helps solidify arithmetic skills and promotes retention. - Utilize Technology:
-Integrate educational apps, interactive websites, or math games to make learning arithmetic engaging and interactive.
-Integrate educational apps, interactive websites, or math games to make learning arithmetic engaging and interactive. - Real-Time Feedback:
-Offer constructive feedback and corrective guidance during arithmetic practice sessions.
-Timely feedback enhances understanding and supports continuous improvement. - Cross-Curricular Connections:
-Integrate arithmetic with other subjects like science, art, or geography to demonstrate its interdisciplinary relevance.
-Making connections across subjects enriches learning experiences and reinforces arithmetic concepts. - Encourage Exploration:
-Foster curiosity by encouraging students to explore patterns, puzzles, and number relationships independently.
-Foster curiosity by encouraging students to explore patterns, puzzles, and number relationships independently.
The Role of Open Minds Campus
At Open Minds Campus, we understand the importance of mastering basic arithmetic for academic success and lifelong learning. Our approach combines innovative teaching methods with personalized attention to cater to diverse learning needs. Here’s how we support students in mastering arithmetic:
Qualified Instructors: Our dedicated teachers provide individualized support to ensure each student grasps arithmetic concepts effectively.
Integrated Curriculum: We integrate arithmetic into our holistic curriculum, connecting it to real-world applications and problem-solving.
Interactive Learning: Through interactive activities and technology-enhanced lessons, we make arithmetic engaging and accessible.
Community Engagement: We foster a supportive learning community where students collaborate and learn from each other’s experiences.
Conclusion
Teaching basic arithmetic is more than just imparting mathematical knowledge; it’s about nurturing essential skills that prepare students for academic success and future endeavours. By employing creative teaching strategies and emphasizing its relevance, we can empower students to excel in arithmetic and beyond. At Open Minds Campus, we are committed to equipping students with the tools they need to thrive in mathematics and in life.